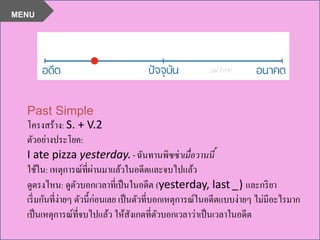
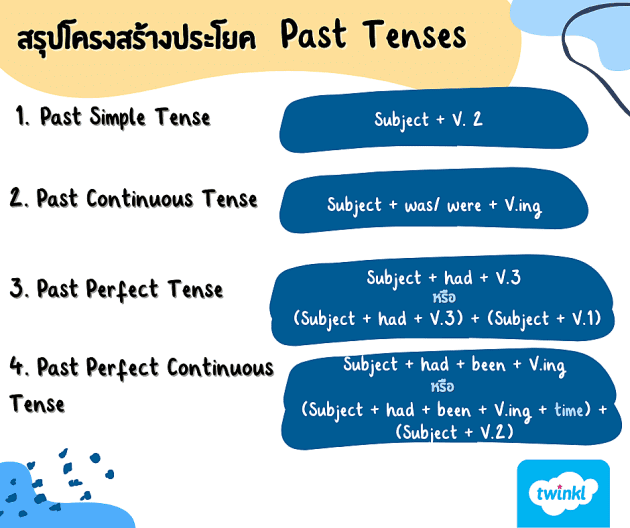
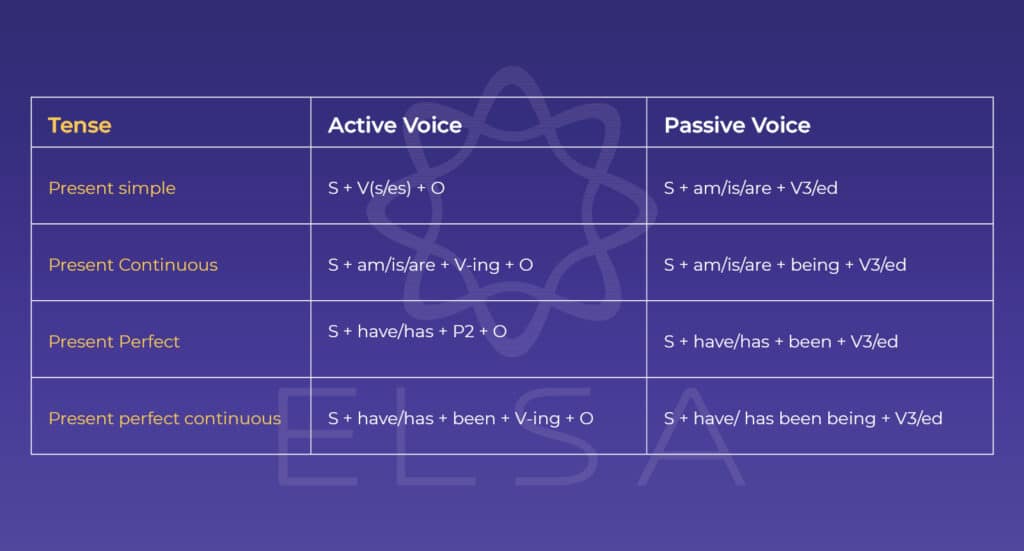
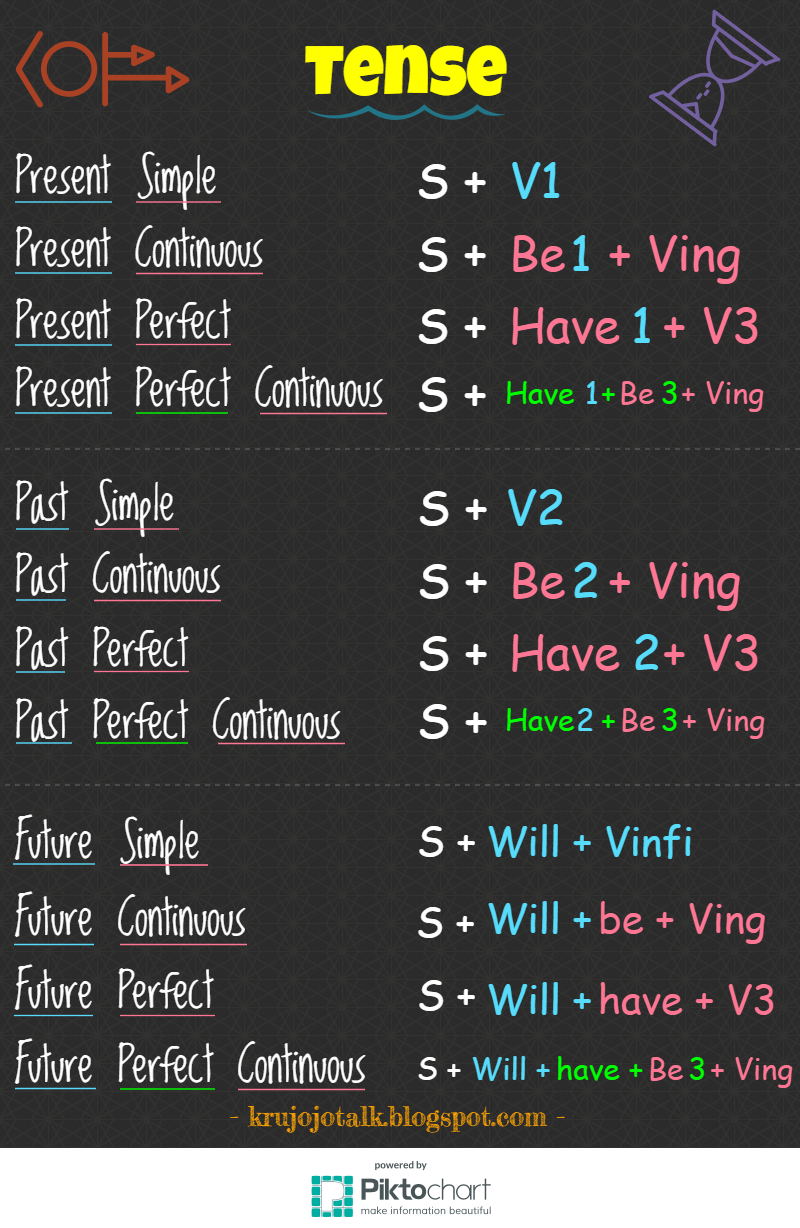
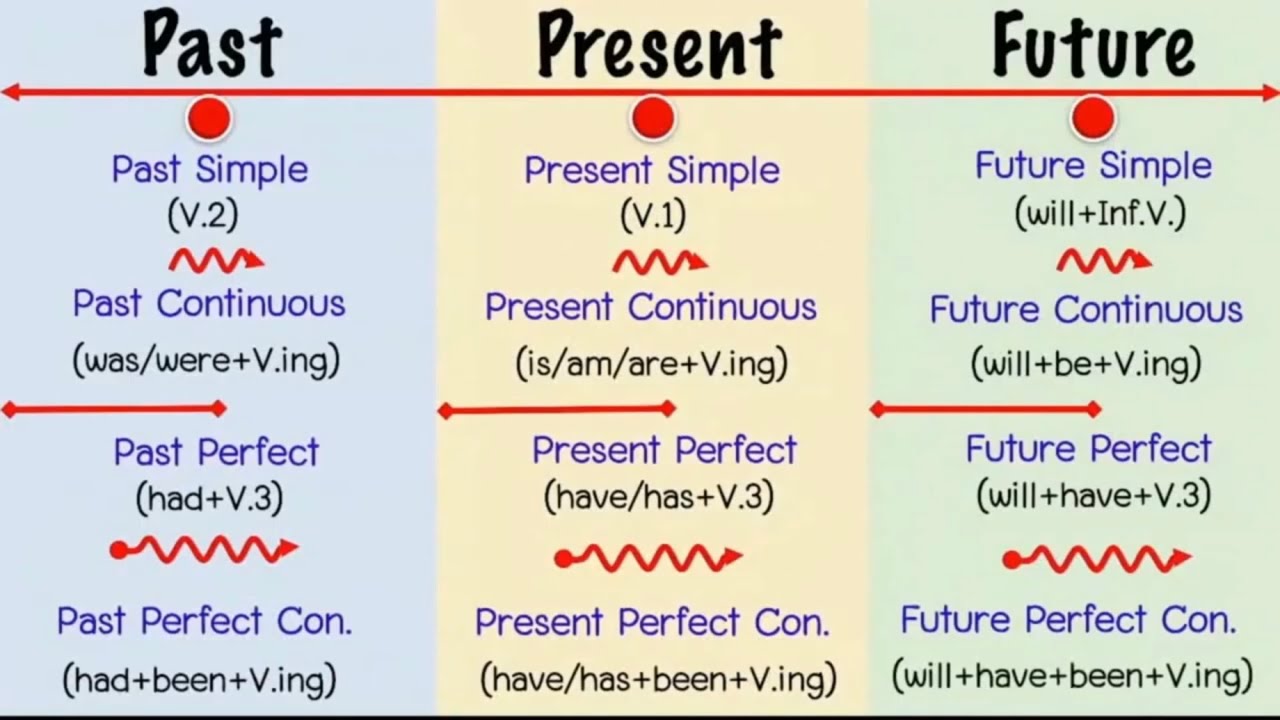
โครงสร้าง Simple Past
Simple Past เป็นรูปเสริมของกริยาในอดีตที่ใช้ในประโยคบวกและประโยคลบ เพื่อแสดงถึงเหตุการณ์หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต โดยมักใช้คำกริยาแบบใช้เป็นอดีตสมบูรณ์ (V2) แต่บางครั้งอาจใช้วลีอื่น ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกริยาตามความเหมาะสมของประโยค
กฎการใช้ Simple Past:
1. ใช้เพื่อแสดงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่เกิดขึ้นและเสร็จสิ้นแล้ว
เช่น I ate dinner last night. (ฉันกินข้าวเย็นเมื่อคืน)
2. ใช้เพื่อแสดงความถี่หรือประจำที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต
เช่น We always went to the beach during summer. (เราเคยไปชายหาดเสมอในช่วงฤดูร้อน)
3. ใช้เพื่ออธิบายสถานะหรือลักษณะเดิมของสิ่งต่าง ๆ
เช่น The car was black. (รถยนต์สีดำ)
ตัวอย่างประโยคที่ใช้ Simple Past:
1. She lived in Thailand for five years. (เธออาศัยอยู่ในประเทศไทยเป็นเวลาห้าปี)
2. He studied English when he was in college. (เขาเรียนภาษาอังกฤษเมื่อเขาอยู่ในมหาวิทยาลัย)
3. They went to the concert last night. (พวกเขาไปงานคอนเสิร์ตเมื่อคืน)
4. I visited my grandparents last summer. (ฉันไปเยี่ยมปู่ย่าของฉันในช่วงฤดูร้อนที่ผ่านมา)
คำกริยาที่ใช้เป็น Simple Past:
คำกริยาช่องที่ 2 (V2) เป็นรูปเสริมที่ใช้ใน Simple Past ในประโยคบวก กฎการเตรียมคำกริยาจะแตกต่างกันไปขึ้นอยู่กับประธานของประโยคว่าเป็นบุรุษ หญิง หรือสิ่งของ (it)
การเตรียมคำกริยา Simple Past ในประโยคบวก:
1. หากประธานเป็นบุรุษและชื่อเอง (กริยา+ed)
เช่น He worked hard yesterday. (เขาทำงานหนักเมื่อวานนี้)
2. หากประธานเป็นบุรุษและไม่ใช่ชื่อเอง (กริยา+ed)
เช่น They played basketball last week. (พวกเขาเล่นบาสเกตบอลสัปดาห์ที่ผ่านมา)
3. หากประธานเป็นหญิง (กริยา+ed)
เช่น She watched a movie with her friends. (เธอดูหนังกับเพื่อนของเธอ)
4. หากประธานเป็นสิ่งของ (it) (กริยา+ed)
เช่น It rained yesterday. (ฝนตกเมื่อวานนี้)
การเตรียมคำกริยา Simple Past ในประโยคลบ:
1. หากกริยามีลักษณะอ้างถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต (กริยาหลัก+ed)
เช่น They said sorry after the argument. (พวกเขาขอโทษหลังการทะเลาะ)
2. หากกริยาเป็นกริยาอนุมานที่ไม่เปลี่ยนรูป (กริยาหลัก)
เช่น He cut his finger while cooking. (เขาเจาะนิ้วของเขาขณะทำอาหาร)
การใช้กริยา to be ในประโยค Simple Past:
กริยา to be ใน Simple Past เกิดจากการเปลี่ยนรูปได้ตามกฎเดียวกับคำกริยาอื่น ๆ
1. กริยา be (am, is, are) ให้เป็น was (สำหรับบุรุษและหญิงในการคำถามและประโยคลบ) และ were (สำหรับบุรุษและหญิงในประโยคบวก)
เช่น She was at home yesterday. (เธออยู่บ้านเมื่อวานนี้)
Were they at the party last night? (พวกเขาอยู่ที่ปาร์ตี้เมื่อคืนหรือไม่)
2. กริยา be (am, is, are) ให้เป็น were สำหรับสิ่งของ (it) ในการคำถามและประโยคบวก
เช่น It was cold yesterday. (อากาศหนาวเมื่อวานนี้)
Were the keys in your bag? (กุญแจอยู่ในกระเป๋าของคุณหรือไม่)
กฎการปรับคำนามและคำกริยาใน Simple Past:
1. ปรับคำนามให้เป็นรูปเต็มเพื่อใช้กับกริยาแบบ Simple Past
เช่น Tom became a doctor last year. (ทอมกลายเป็นหมอในปีที่แล้ว)
2. ปรับคำกริยาให้เป็นรูป V2 เพื่อใช้กับกริยาแบบ Simple Past
เช่น They ate lunch together. (พวกเขากินข้าวกลางวันด้วยกัน)
การใช้ Simple Past ร่วมกับคำสองคำ:
Simple Past สามารถใช้ร่วมกับคำสองคำที่เกี่ยวข้องได้
การใช้ Simple Past กับคำสองคำที่เกี่ยวข้อง:
1. หากคำสองคำอยู่ในรูปแบบของกริยาและ V2 (กริยาและกริยา)
เช่น She played and won the game. (เธอเล่นและชนะเกม)
2. หากคำสองคำแสดงถึงเหตุการณ์-ผลลัพธ์ (กริยาและV3)
เช่น He studied hard and passed the exam. (เขาเรียนหนักและสอบผ่าน)
การใช้ Simple Past กับคำสองคำที่เป็นคู่สัมพันธ์:
1. คำสองคำที่เป็นคู่สัมพันธ์ให้ใช้ Simple Past ทั้งคู่ (ด้วยขั้นตอนเดียวกันหรือลำดับเหมือนกัน)
เช่น She neither ate nor drank anything. (เธอไม่ได้กินหรือดื่มอะไรเลย)
2. หากคำสองคำที่เป็นคู่สัมพันธ์มีหนึ่งคำอยู่ใน Simple Past และคำอีกคำเป็นปัจจุบัน (Past Simple + Present)
เช่น She knew but didn’t tell anyone. (เธอรู้แต่ไม่มีใครบอก)
ประโยชน์และการนำไปใช้:
การเรียนรู้และการใช้ Simple Past ในการเขียนและสื่อสารอย่างถูกต้องมีประโยชน์อย่างมาก ต่อไปนี้คือประโยชน์ที่สำคัญของการใช้ Simple Past:
1. การใช้ Simple Past ในการเล่าเรื่องราว:
Simple Past ช่วยให้เราสามารถเล่าเรื่องราวของเหตุการณ์ในอดีตได้อย่างราบรื่นและถูกต้อง เช่น “I visited Paris last summer. The city was beautiful and I saw many famous landmarks.”
2. การใช้ Simple Past เพื่ออธิบายเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต:
เราสามารถใช้ Simple Past เพื่ออธิบายเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีตและสิ้นสุดลง เช่น “I left my job and started a new career.”
3. การใช้ Simple Past เพื่อเปรียบเทียบระหว่างเหตุการณ์ในอดีตและปัจจุบัน:
เราสามารถใช้ Simple Past เพื่อเปรียบเทียบเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีตกับสถานการณ์ปัจจุบัน เช่น “When I was a child, I used to play outside all day. Now, I spend most of my time indoors.”
การใช้ Simple Past ในภาษาไทยมีความสำคัญและส่งผลที่มีนัยสำคัญต่อการเขียนและสื่อสารในทางที่ถูกต้อง การเรียนรู้หรือศึกษาโครงสร้างและการใช้ Simple Past จึงเป็นสิ่งสำคัญในการพัฒนาทักษะการใช้ภาษาไทยของเราเอง
สรุปวิธีใช้ Past Simple Tense แบบเข้าใจง่ายๆ
คำสำคัญที่ผู้ใช้ค้นหา: โครงสร้าง simple past past simple tense ตัวอย่างประโยค, ตัวอย่างประโยค past simple tense 20 ประโยค, Past Simple Tense, past simple คืออะไร, Past Simple Tense คือ, ประโยค past simple tense ในชีวิตประจําวัน, Past Continuous, past continuous tense ตัวอย่างประโยค
รูปภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อ โครงสร้าง simple past

หมวดหมู่: Top 97 โครงสร้าง Simple Past
Past Simple เติมอะไร
In the Thai language, verb conjugation plays a vital role in expressing the past tense. One important aspect of Thai grammar is the use of “เติมอะไร” or “tèrm arai,” which literally translates to “fill in what.” It refers to the process of adding a specific word or phrase after a verb in order to convey the past simple tense. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Past Simple เติมอะไร and provide a comprehensive understanding of its usage.
Understanding Thai Verb Conjugation:
Before we delve into Past Simple เติมอะไร, let’s briefly touch upon Thai verb conjugation. Unlike languages like English where verbs undergo changes based on subject pronouns (e.g., “I go” vs. “he goes”), Thai verbs remain unchanged regardless of the subject. The conjugation of verbs in Thai primarily focuses on conveying different tenses, such as the past, present, or future.
The Past Simple Tense in Thai:
When it comes to the past simple tense in Thai, the “เติมอะไร” rule comes into play. In its simplest form, the structure of a sentence in the past simple tense can be described as follows:
[Subject] + [Verb] + [Object] + เติมอะไร
Here, the verb remains in its infinitive form, without any changes based on the subject. However, what follows after the verb—เติมอะไร—determines the tense, in this case, the past tense.
Common Words Used with เติมอะไร:
Now let’s look at some of the common words that are used with เติมอะไร to express the past simple tense:
1. เมื่อวัน [meûa wan] – When
This phrase is often placed before เติมอะไร to indicate the specific time or date in the past when an action occurred. For example:
ผมเข้าร้านอาหารเมื่อวันเสาร์ที่แล้วเติมอะไร? (I went to the restaurant last Saturday. What did you order?)
2. เมื่อวาน [meûa waan] – Yesterday
เมื่อวาน is a commonly used word to denote the past simple tense. When combined with เติมอะไร, it refers to an event or action that took place yesterday. For example:
เมื่อวานคุณเห็นหนังเรื่องไหนเติมอะไร? (Yesterday, which movie did you watch?)
3. ตอน [dtawn] – When
Similar to เมื่อวัน, ตอน is used to mark a specific time or period in the past. It can be followed by เติมอะไร to convey the past simple tense. For example:
ตอนเช้าวันที่แล้วคุณทำอะไรเติมอะไร? (What did you do yesterday morning?)
FAQs about เติมอะไร:
Q: Can เติมอะไร be used for other tenses?
A: No, เติมอะไร is specifically used to express the past simple tense in Thai. For other tenses, different words or conjugations are required.
Q: Can I use เติมอะไร with any verb?
A: Yes, เติมอะไร can be used with any verb in its infinitive form to indicate the past simple tense. However, it is essential to choose the appropriate word to complete the sentence correctly.
Q: Are there any other ways to express the past tense in Thai?
A: Yes, apart from เติมอะไร, the past tense can also be conveyed using specific time expressions or particles such as แล้ว [léaw] or ก็ [gôr]. These particles are added at the end of a sentence to indicate the past actions.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using เติมอะไร?
A: One common mistake is adding เติมอะไร after a verb that is already in the past tense form. Another mistake is neglecting to use เติมอะไร at all, which may result in confusion for the listener or reader.
In conclusion, understanding Past Simple เติมอะไร and mastering its usage is essential for effectively expressing the past tense in Thai. By employing the right time expressions or words, learners of Thai can confidently communicate about past events or actions. So, the next time you want to talk about what you did in the past, remember to fill in the blank with เติมอะไร!
Past Simple ยังไง
The Past Simple tense, or กาลอนุกรมอดีต (Kaan Anukam A-dit) in Thai, is an essential aspect of the Thai language. It is used to describe actions, situations, or events that have already occurred in the past. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of Past Simple ยังไง, including its structure, usage, and common misconceptions.
Structure of Past Simple ยังไง:
To form the Past Simple tense, Thai verbs undergo specific changes depending on whether they end with a consonant or vowel sound. Let’s look at the structure for each case:
1. Verbs ending with a consonant sound:
For verbs that end with a consonant sound, such as กิน (kin, to eat) or เดิน (den, to walk), the suffix -ด (-d) is added to the verb root. For example:
กิน (to eat) → กิน + ด (ate) → กินด (ate)
เดิน (to walk) → เดิน + ด (walked) → เดินด (walked)
2. Verbs ending with a vowel sound:
For verbs that end with a vowel sound, such as เปล่ง (bplen, to pour) or เสนอ (senu, to propose), the root verb remains unchanged, and the suffix -เ (-e) is added. For example:
เปล่ง (to pour) → เปล่งเ (poured) → เปล่งเ (poured)
เสนอ (to propose) → เสนอเ (proposed) → เสนอเ (proposed)
Usage of Past Simple ยังไง:
The Past Simple tense is used to indicate an action, event, or state that took place in the past and is now completed. Here are the different ways the Past Simple tense can be used:
1. To describe actions or events in the past:
กาลอนุกรมอดีต is commonly used to describe actions or events that occurred in the past. For example:
เมื่อวานฉันกินข้าวที่ร้านอาหาร (Yesterday, I ate rice at the restaurant)
2. To express repeated actions in the past:
The Past Simple tense can also be used to express actions that occurred repeatedly in the past. For example:
เขานอนเก้าทุ่มทุกวัน (He used to sleep at 9 p.m. every day)
3. To narrate past events:
When telling a story or narrating past events, Thai speakers often use the Past Simple tense. For example:
ผมเห็นคุณเค้าด้วยเสน่ห์เล่ห์ (I saw him/her with enchanting beauty)
4. To express wishes or regrets:
In Thai, the Past Simple tense can be used to express wishes or regrets about the past. For example:
เขาอยากไปพบคุณสุดแสน (He/She wished/longed to meet you)
Common Misconceptions about Past Simple ยังไง:
1. Past Simple ยังไง is always the same as the English past tense:
While the Past Simple tense in Thai and the past tense in English often correspond in their basic functions, it is crucial to remember that they can differ in certain aspects. Thai verbs do not have tense inflections to indicate time, but rather rely on time indicators and contextual cues.
2. Past Simple ยังไง is the only way to express the past tense in Thai:
Although Past Simple ยังไง is commonly used to describe past events, it is not the only way to express the past tense in Thai. Thai also has the Past Continuous tense (กาลอนุกรมอดีตต่อเนื่อง), Past Perfect tense (กาลอนุกรมอดีตแนบท้าย), and other past tense constructions to convey different nuances of time.
FAQs about Past Simple ยังไง:
Q1: Are there any irregular verbs in Past Simple ยังไง?
A1: No, there are no irregular verbs in Past Simple ยังไง. The suffixes -ด (-d) or -เ (-e) are added to the verb roots consistently based on the ending sound.
Q2: Can the Past Simple tense be used with time indicators?
A2: Yes, it is common to use time indicators, such as เมื่อวาน (yesterday) or วันที่ผ่านมา (the previous day), in conjunction with the Past Simple tense to clearly establish the past time frame.
Q3: Is the Past Simple tense used in formal or informal settings?
A3: The Past Simple tense can be used in both formal and informal settings. Its usage depends on the context and level of formality required.
Q4: Can the Past Simple tense be used to express future events?
A4: No, the Past Simple tense specifically refers to actions or events that have already transpired in the past. For future events, other tenses like กาลอนุกรมอนาคต (Future Simple) should be used.
In conclusion, the Past Simple tense (กาลอนุกรมอดีต) is an essential component of the Thai language to express actions, events, or states in the past. Its structure varies based on the ending sound of the verb, and it can be used in various situations, from describing past events to expressing wishes or regrets. Understanding the correct usage of the Past Simple tense in Thai is crucial for effective communication in the language.
ดูเพิ่มเติมที่นี่: lasbeautyvn.com
Past Simple Tense ตัวอย่างประโยค
Past Simple Tense เป็นเหมือนกับช่วงเวลาที่ผ่านไปแล้วในอดีต ซึ่งใช้เชื่อมหรืออธิบายกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต โดยบอกถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงในอดีต พร้อมกับช่วยให้เราสามารถเล่าเรื่องราวหรือสอบถามข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับอดีตได้อย่างแน่นอน
การใช้ Past Simple Tense ในภาษาอังกฤษจำเป็นต้องเรียนรู้การใช้คำกริยาแสดงอดีตที่เป็นต้นฉบับ รูปแบบทั่วไปของคำกริยาในอดีตจะมีเพียงสรีระเดียว โดยในประโยคปกติ เราจะเพิ่ม -ed เข้าไปที่ปลายคำกริยา ตัวอย่างประโยคประกอบใน Past Simple Tense ได้แก่
1. She worked hard all day yesterday. (เธอทำงานหนักทั้งวันเมื่อวาน)
2. He studied French for three years. (เขาเรียนภาษาฝรั่งเศสเป็นเวลาสามปี)
3. They watched a movie at the cinema last night. (พวกเขาดูหนังที่โรงหนังเมื่อคืน)
เพราะรูปแบบการใช้งานนี้มีลักษณะแล้วแต่ละภาษา จึงมีคำใช้ช่วยเติมความเน้นจำนวนมาให้เห็นชัดเจน เช่น
1. I did my homework yesterday. (ฉันทำการบ้านเมื่อวาน)
2. He wrote two letters last night. (เขาเขียนจดหมายสองฉบับเมื่อคืน)
3. She visited her grandparents on Sunday. (เธอไปเยี่ยมปู่ย่าบ้านเมื่อวันอาทิตย์)
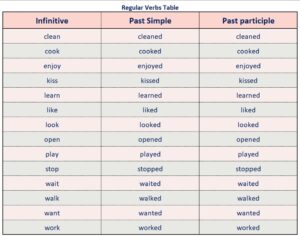
การเปลี่ยนแปลงคำกริยาใน Past Simple Tense เกิดขึ้นหากคำกริยาที่เรียกใช้นั้นเป็นสิ่งชี้ซ้ำ (Irregular Verbs) อย่างตัวอย่าง
1. She went to the park yesterday. (เธอไปเที่ยวที่สวนสาธารณะเมื่อวาน)
2. He ate lunch at the restaurant. (เขากินอาหารเที่ยงที่ร้านอาหาร)
3. They swam in the sea last summer. (พวกเขาว่ายน้ำที่ทะเลในฤดูร้อนที่ผ่านมา)
ในบางกรณี เราจำเป็นต้องใช้กริยาช่วยเติม (Auxiliary Verbs) เช่น did, didn’t, เพื่อทำให้ประโยคเป็นรูปช่องที่ 2 (second conditional) 3 (third conditional) วิธีการใช้งานประมาลเจตที่ถูกต้องยังไง? ตัวอย่างประโยคประกอบเพื่อให้เห็นภาพชัดเจน
1. Did you see the movie last night? (คุณได้ดูหนังเมื่อคืนไหม?)
2. We didn’t eat dinner at the restaurant. (เราไม่มีอาหารเย็นที่ร้านอาหาร)
3. She didn’t go to the party last weekend. (เธอไม่ได้ไปงานเลี้ยงวันสุดสัปดาห์ที่ผ่านมา)
ประโยคประกอบใน Past Simple Tense ต่างจะมีลักษณะการใช้ที่แตกต่างกันไป การเล่าเรื่องราวในอดีต การสอบถามและให้ข้อมูลรอบคอบเป็นต้น ด้วยเหตุนี้ เราได้รวบรวมคำถามที่พบบ่อยเกี่ยวกับ Past Simple Tense เพื่อช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจได้ลึกซึ้งกว่าเดิม
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is the difference between Present Simple Tense and Past Simple Tense?
A1: Present Simple Tense เชื่อมหรืออธิบายการกระทำในปัจจุบัน ในขณะที่ Past Simple Tense เชื่อมหรืออธิบายการกระทำที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต
Q2: Can we use irregular verbs in Past Simple Tense?
A2: Yes, irregular verbs are commonly used in Past Simple Tense. However, the conjugation of irregular verbs does not follow the regular -ed pattern and needs to be memorized individually.
Q3: Are there any specific time expressions that are commonly used with Past Simple Tense?
A3: Yes, there are many time expressions that can be used with Past Simple Tense to indicate the time of the action or event. Some common time expressions include yesterday, last night, last week, last year, ago, etc.
Q4: Can we use Present Simple Tense and Past Simple Tense together in the same sentence?
A4: Yes, it is possible to use both tenses in the same sentence when describing a sequence of events. For example: “I usually drink coffee in the morning, but yesterday I had tea.”
Q5: How do we form negative sentences in Past Simple Tense?
A5: To form negative sentences in Past Simple Tense, we use the auxiliary verb “did” followed by “not” and the base form of the main verb. For example: “She did not go to the party last night.”
Q6: Is there any difference between regular verbs and irregular verbs in Past Simple Tense?
A6: Yes, regular verbs follow the -ed pattern, whereas irregular verbs have their own unique past tense forms that do not follow a specific pattern. Regular verbs are more common and easier to conjugate compared to irregular verbs.
In conclusion, the Past Simple Tense is commonly used to describe actions or events that occurred in the past. By understanding the rules and patterns of using this tense, you can effectively communicate and express past actions in English. It is important to practice and familiarize yourself with the different forms of regular and irregular verbs to enhance your English language skills.
ตัวอย่างประโยค Past Simple Tense 20 ประโยค
Past Simple Tense เป็นรูปเวลาที่ใช้ในการอธิบายเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีตหรือสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นและจบแล้วในอดีต ในภาษาไทยจะใช้คำกริยาช่วย “ไว้” นำหน้ากริยาแสดงเวลาอดีต
ดังนี้คือตัวอย่างประโยค Past Simple Tense 20 ประโยคในภาษาไทย:
1. เมื่อวานผมเดินไปที่ร้านค้า Yesterday, I walked to the store.
2. เขาเข้ามาในห้องเรียนอย่างเงียบ He entered the classroom quietly.
3. เมื่อสดชื่นเขาแชร์ข่าวว่าได้เป็นผู้ชนะกับเพื่อนสักคน He happily shared the news of his victory with a friend.
4. คุณเป็นกันเดียวกับผมและทำให้ผมรู้สึกดี You were on my side and made me feel good.
5. เมื่อซื้อหนังสือวางไว้บนโต๊ะอย่างรวดเร็วหน่อย She quickly put the book on the table.
6. เขาไม่รู้สึกเสียใจว่าไม่ได้ชนะ He didn’t feel sad that he didn’t win.
7. เมื่อตอนเช้าคุณเล่าเรื่องสนุกแก่ฉันได้อย่างมีความสุข In the morning, you told me a fun story with great joy.
8. จิตใจของเขาเต้นรำอย่างรวดเร็ว His heart beat fast.
9. เมื่อเดินไปด้านหน้าคุณสังเกตเห็นสิ่งต่างๆ When you walked forward, you noticed various things.
10. เขาจำได้ว่าในอดีตเขาเคยเป็นเทพนักสืบ He remembered that in the past, he used to be a great detective.
11. พ่อของฉันซื้อสินค้าออนไลน์เมื่อวาน My father bought products online yesterday.
12. ฉันไปเที่ยวไปที่พิพิธภัณฑ์เมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้ว I visited the museum last week.
13. เมื่อวานนี้ฉันโทรไปหาเพื่อน I called my friend yesterday.
14. เธอทำอะไรเมื่อวานค่ะ? What did she do yesterday?
15. เมื่อตื่นนอนมาเมื่อวานฉันทำอะไรไปบ้าง? What did I do when I woke up yesterday?
16. เมื่อวานนี้เขาเหนื่อยมากค่ะ She was very tired yesterday.
17. เมื่อวานนี้ฉันดูหนังได้ I watched a movie yesterday.
18. เมื่อวานผมทำงานการบ้าน I did my homework yesterday.
19. เมื่อวานนี้ฉันเป็นเสียงสูง I raised my voice yesterday.
20. เมื่อวานนี้คุณไม่ได้รับรู้เรื่องสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นคุณ Didn’t you know what happened yesterday?
คำถามที่พบบ่อย:
Q: Past Simple Tense คืออะไร?
A: Past Simple Tense เป็นรูปเวลาที่ใช้ในการอธิบายเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีตหรือสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นและจบแล้วในอดีต ในภาษาไทยจะใช้คำกริยาช่วย “ไว้” นำหน้ากริยาแสดงเวลาอดีต
Q: ในภาษาไทย Past Simple Tense สร้างอย่างไร?
A: ในภาษาไทย Past Simple Tense จะสร้างโดยการใช้คำกริยาช่วย “ไว้” นำหน้ากริยาแสดงเวลาอดีต
Q: วิธีใช้ Past Simple Tense ที่ถูกต้องคืออย่างไร?
A: Past Simple Tense ใช้กริยาตรงกับประธานของประโยคที่เป็นบุคคลเดียว หรือเพียงรูปเดียวกับตำแหน่งการกรุณาว่าง เช่น “He walked to the store” (เขาเดินไปที่ร้านค้า)
Q: ในกรณีใดที่ต้องเพิ่ม “did” นำหน้ากริยาใน Past Simple Tense?
A: ต้องเพิ่ม “did” นำหน้ากริยาในกรณีที่ประธานของประโยคเป็นชื่อตัวเอง หรือเท่ากับชื่อตัวเอง เช่น “Did you take a walk yesterday?” (คุณไปเดินเล่นเมื่อวาน?)
Q: อาจใช้ Present Simple Tense แทน Past Simple Tense ในบางกรณีได้หรือไม่?
A: ไม่สามารถใช้ Present Simple Tense แทน Past Simple Tense ได้ เนื่องจาก Present Simple Tense ใช้อธิบายเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในปัจจุบันหรืออนาคต ไม่ใช่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต
การใช้ Past Simple Tense ในภาษาไทยจำเป็นสำหรับการเล่าเรื่องราวหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต ผู้เรียนสามารถฝึกใช้ความรู้ที่ได้จากตัวอย่างประโยคเหล่านี้ในการพัฒนาทักษะในการสื่อสารในภาษาไทยได้
Past Simple Tense
In Thai grammar, the past simple tense is an essential aspect of communication. Understanding how to properly use this tense is crucial for conveying past events and actions accurately. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the past simple tense in Thai, including its formation, usage, and common pitfalls. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced learner, this guide will help you master the past simple tense in Thai.
Formation of Past Simple Tense
To form the past simple tense, you typically add the word “ได้” (dâi) before the main verb. For instance, if the main verb is “ไป” (bpai), meaning “to go,” the past simple form would be “ไปได้” (bpai dâi), translating to “went.” It is worth noting that the structure of Thai grammar is fairly straightforward, without many exceptions or complex conjugations. However, there are a few irregular verbs that require different forms in the past tense, which we will cover in more detail below.
Usage of Past Simple Tense
1. Describing Completed Actions
The primary function of the past simple tense is to express completed actions in the past. It is used to narrate events that happened at a specific point in time and have already concluded. For example:
ฉันอ่านหนังสือเมื่อวาน (chan aa-năng-suue muua-waan) – I read a book yesterday.
2. Expressing Past Duration
In addition to individual actions, the past simple tense can also be used to indicate the duration of past events. By using adverbs like “เมื่อ” (muua), meaning “when,” or “โดยรวม” (dooai-ruam), meaning “in general,” you can provide more context to your statements. For instance:
เขาซื้อข้าวที่ตลาดเมื่อเช้า (khao sue khaao thii talaat muua chaao) – He bought rice at the market this morning.
3. Expressing Past Habits
When discussing past habits or repeated actions, the past simple tense is commonly employed. In these cases, time expressions such as “เสมอๆ” (sà-muh-sà-muh), meaning “always,” or “บ่อยๆ” (bòi-bòi), meaning “often,” are used. For example:
แม่ชอบเตะบอลให้บ้านหลังเคย (mâe chôp tét bawn hâi bâan-lăng keoie) – My mother used to kick a ball behind the house.
Irregular Verbs in Past Simple Tense
While the majority of Thai verbs follow the regular formation rules mentioned earlier, there are a few irregular verbs that require specific past tense forms. Some commonly used irregular verbs include:
1. กิน (gin) – to eat: past form – กิน (gin)
2. ดื่ม (deum) – to drink: past form – ดื่ม (deum)
3. เปลี่ยน (bplìan) – to change: past form – เปลี่ยน (bplìan)
4. เสีย (sǐa) – to lose: past form – เสีย (sǐa)
It is crucial to remember these exceptions and practice their past forms, as they differ from the general rule.
FAQs
Q1. Are there any other ways to express the past in Thai?
A1. Yes, apart from the past simple tense, Thai language also employs the use of time-related adverbs and particles to indicate past events. These include words like “ก่อน” (gòn), meaning “before,” and “หลังจาก” (lang-jaak), meaning “after.”
Q2. Are there any exceptions to the regular formation of the past simple tense?
A2. As mentioned earlier, there are a few irregular verbs in Thai that do not follow the standard formation rules. These irregular verbs have specific past tense forms that differ from the regular “ได้ + verb” structure.
Q3. Can I use the past simple tense to describe ongoing past events?
A3. No, the past simple tense is reserved for describing completed past actions or events. To describe ongoing past actions, you can use the past continuous tense using the word “กำลัง” (gam-lang) before the verb.
Q4. How can I practice using the past simple tense in Thai?
A4. To effectively practice the past simple tense, engage in conversations, read books or articles in Thai, and listen to Thai songs or movies. Actively incorporating the tense in your daily language practice will reinforce your understanding and fluency.
In conclusion, the past simple tense plays a vital role in Thai grammar, allowing speakers to accurately convey past events and actions. By understanding the formation, usage, and irregular verbs associated with the past simple tense, you will be better equipped to communicate effectively in Thai. Practice and immerse yourself in the language to solidify your comprehension, and soon you will be able to confidently travel back in time with your Thai linguistic skills.
พบ 22 ภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อ โครงสร้าง simple past.



















![IELTS Tips] การใช้ Past Simple และ Past Perfect Simple (ตอนที่ 1) - IELTS Ielts Tips] การใช้ Past Simple และ Past Perfect Simple (ตอนที่ 1) - Ielts](https://www.oxbridge.in.th/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/past_simple-400x285.gif)




















ลิงค์บทความ: โครงสร้าง simple past.
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโพสต์หัวข้อนี้ โครงสร้าง simple past.
- หลักการใช้ Past simple tense ฉบับเข้าใจง่าย – GrammarLearn
- Simple past tense | EF | ประเทศไทย – EF Education First
- Past Simple Tense คืออะไร มีหลักการใช้งาน และโครงสร้างประโยค …
- สรุปวิธีการใช้ Past Simple ฉบับรวบรัด – Globish
- หลักการใช้ Past Simple Tense ง่าย…มากๆ ใช้กริยาเดียวกันหมด …
- โครงสร้าง Past Simple Tense, Past Continuous Tense … – LMS2
- Past Simple Tense คืออะไร มีหลักการใช้งาน และวิธีการสร้าง …
- สรุปวิธีการใช้ Past Simple ฉบับรวบรัด – Globish
- Past Simple Tense คืออะไร มีหลักการใช้งาน และโครงสร้างประโยค …
- Past Simple Tense คืออะไร มีหลักการใช้งาน และวิธีการสร้างประโยค …
- Present Simple Tense คืออะไร โครงสร้างประโยค วิธีใช้
- วิธีใช้ Past Tense ในการเล่าเรื่อง ฉบับเข้าใจง่ายที่สุดในโลก
- หลักการใช้ Past Simple Tense – Engduo Thailand
ดูเพิ่มเติม: https://lasbeautyvn.com/category/digital-studios